TOP > 生物多様性センターの国際協力 > ESABII > About us > Overview

Overview
Background
In 1992, the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) was adopted as an international framework for the conservation of biodiversity as well as for the utilization of biological resources in a sustainable manner. The 4th meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD COP4) in 1998 decided to implement the Global Taxonomy Initiative (GTI). The CBD COP10 held in Nagoya City, Aichi Prefecture, Japan adopted the Strategic Plan for Biodiversity 2011-2020 (Aichi Biodiversity Targets), among which Target 19 was set to improve the knowledge, science base and technologies related to biodiversity.
The importance of taxonomy has increasingly been recognized as a global issue. While East and Southeast Asia have a much higher level of biodiversity than other parts of the world, there are insufficient numbers of personnel with the taxonomic knowledge and capacity required for biodiversity conservation. Moreover, information on biodiversity is limited and scattered, and information infrastructure for biodiversity is not fully developed in the region.
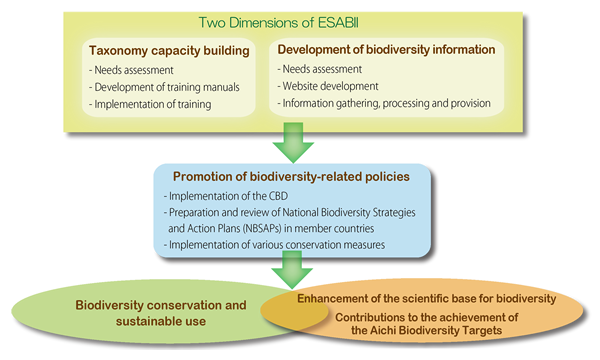
What is ESABII?
The East and Southeast Asia Biodiversity Information Initiative (ESABII) was launched to pursue capacity building in taxonomy and the development of an information system on biodiversity in East and Southeast Asia in order to contribute to the promotion of biodiversity conservation and the implementation of the CBD Strategic Plan in the area.