
TOP > 生物多様性センターの国際協力 > ESABII > Database > Threatened Mammal Species Database > Presbytis chrysomelas

Presbytis chrysomelas
Taxonomy (Name)
| Class | MAMMALIAIUCN | |
|---|---|---|
| Order | DIPROTODONTIAIUCN | |
| Family | CERCOPITHECIDAEIUCN | |
| Scientific Name | Presbytis chrysomelasIUCN | |
| Author | (Muller, 1838)IUCN | |
| Synonyms | Presbytis arwasca Miller, 1934 Presbytis femoralis (Muller, 1838) ssp. chrysomelas IUCN |
|
| Common Name | Sarawak Surili, Bornean Banded LangurIUCN | |
| Local name | Brunei Darussalam | |
| Cambodia | ||
| China | ||
| Indonesia | ||
| Japan | ||
| Lao PDR | ||
| Malaysia | ||
| Myanmar | ||
| Mongolia | ||
| Philippines | ||
| Singapore | ||
| Republic of Korea | ||
| Thailand | ||
| Vietnam | ||
Picture
Distribution, Range
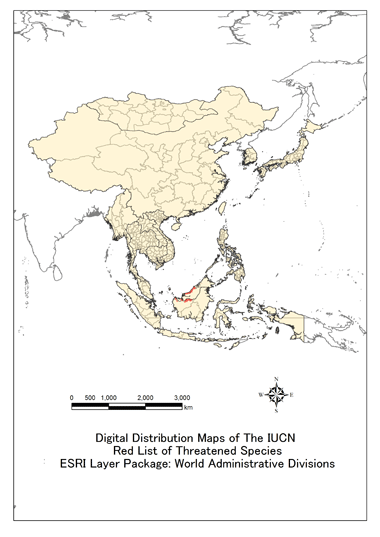
This species is endemic to the island of Borneo, it occurs in Brunei, Indonesia (Kalimantan) and Malaysia (Sabah and Sarawak). It is found north and northeast of the Kapuas River in northwestern Kalimantan, and through Sarawak (mainly in coastal areas) and Brunei as far as Melalap, Sabah (Groves 2001). The species is found only in remaining habitat within its extent of occurrence; much of its mapped range is historical. There is some confusion about where this species still remains, as many of the records are also historical.
P. c. chrysomelas:
Occurs in western Brunei, northwestern Kalimantan (northeast of the Kapuas River) and western Sarawak, as far as the IV Division of Sarawak (Groves 2001).
P. c. cruciger:
Ranges from the Baram District (in northeastern Sarawak) to Sabah (Groves 2001).
Map

Country
| Brunei Darussalam | |
|---|---|
| Cambodia | |
| China | |
| Indonesia | |
| Japan | |
| Lao PDR | |
| Malaysia | |
| Myanmar | |
| Mongolia | |
| Philippines | |
| Singapore | |
| Republic of Korea | |
| Thailand | |
| Vietnam |
Status
International Status
IUCN Red List Category
CRIUCN
Justification
This species is listed as Critically Endangered as it is only known from five sites, where populations have been reduced by approximately 80% over the past 30 years (approximately three generations). In addition, the area of occupancy has been reduced dramatically. This species was once considered common, thus there is great concern that it is among the rarest primates in the region after 100 years of persecution and habitat loss. This is now considered one of the rarest primates in the world. It occurs in less than 5% of its historic range. Additional conservation measures are urgent as this species could go extinct if current trends continue.
CITES
CMS
National Status
| Country | Category | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Brunei Darussalam | ||
| Cambodia | ||
| China | ||
| Indonesia | ||
| Japan | ||
| Korea | ||
| Lao PDR | ||
| Malaysia | ||
| Mongolia | ||
| Myanmar | ||
| Philippines | ||
| Singapore | ||
| Thailand | ||
| Vietnam |
Ecology Discription
Appearance
Habitat
This species is found in swamp and lowland forests, as well as mangrove. Group size is 3-7 individuals (J. Hon pers. comm.).
Population size
This species was reported as common in the early 20th century (Baccari 1904; Banks 1931), in areas where today it no longer occurs. Recent records are from five sites: Maludam National Park (Malaysia); Samunsam Wildlife Sanctuary (Malaysia); Similajau National Park (Malaysia); Tanjung Datu National Park (Malaysia); the Lingga area of Sarawak (Malaysia); and possibly Betung Kerihun National Park (Indonesia) (J. Hon pers. comm.). Combined population estimates from these sites are very low (approximately 200-500 individuals) (J. Hon and V. Nijman pers. comm.).
Behavior
Diet
Reproduction
Threat
Major Threat(s)
Habitat conversion has historically been the main threat to this species, resulting in its disappearance from most of its former range. It has in particular been affected by expanding plantations, especially oil palm, in recent years.
Conservation and Measurement
International
This species is listed under CITES Appendix II.IUCN
National
Conservation law
| Country | Status | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Brunei Darussalam | Part B:Other animals the export of which is forbidde except under licence | Law of Brunei Chapter 102 Wild Life Protection 10 of 1978 |
| Cambodia | ||
| China | ||
| Indonesia | ||
| Japan | ||
| Korea | ||
| Lao PDR | ||
| Malaysia | Protected Wild Animal, Part Ⅱ Game Animal(as Banded Leaf Monkey(Presbytis melalophos)) | Law of Malaysia Act 76, Protection of Wild Life Act 1972 (Amend. 2006) |
| Mongolia | ||
| Myanmar | ||
| Philippines | ||
| Singapore | ||
| Thailand | ||
| Vietnam |
Protected Area
The majority of the remaining populations are found in national parks. The species is protected in Sarawak. Further research and surveys are necessary to confirm the persistence and population size of the five remaining sites, which include Maludam National Park, Samunsam Wildlife Sanctuary, Similajau National Park, and Tanjung Datu National Park in Malaysia, and possibly Betung Kerihun National Park in Indonesia. It is present as well in the Lingga area of Sarawak, which has recently been proposed as a protected area.
Other Coservation Projects
Citation
Groves, C. P. 2001. Primate taxonomy. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, DC, USA.
Muller, S. 1838. Over eenige nieuwe zoogdieren van Borneo. Tijdschrift voor Natuurlijke Geschiedenis en Physiologie 5: 134?150.
Payne, J. C. M., Francis, C. M. and Phillipps, K. 1985. A field guide to the mammals of Borneo. The Sabah Society, Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia.
Thomas, O. 1892. Description of a remarkable new Semnopithecus from Sarawak. Annals and Magazine of Natural History 10: 475-477.
